Cyber Security
Virus Bulletin: Old malware never dies – it just gets more targeted – We Live Security
Published
2 years agoon

Putting a precision payload on top of more generic malware makes perfect sense for malware operators
Virus Bulletin this year brought a fresh batch of amped-up, refreshed malware with lots more horsepower and devilish amounts of custom-tailored targeting. From singled-out political activist individual targets to regionalized targets, malware’s aim is getting better.
Putting a precision payload on top of more generic malware makes sense. Why forklift a whole new stack under your exploit when you can just replace the tip of the spear to best effect? For example, Lyceum seems like a redo after Talos and others got wise to previous operations. But much of the secret sauce came from threat actors just tacking on some interesting bits like turning the IP octets into four ASCII encoded commands for the C&C server, which is kind of cool.
For malware operators, there’s a certain deniability in using standard tools, which thwarts malware analysis efforts if much of the evidence is a mash-up of standard tools. How would you prove who did it with high confidence? This year we also saw plenty of “technical overlap” where shifts from prior POS hack malware to “big game hunting” ransomware basically follow the money with the smallest possible effort.
Another trend: Highly targeted, nation-state-flavored malware. Political activists in particular are a perennial target (thanks Amnesty International for insight following on from Netscout/Bitdefender work), with hackers tempting targets via malicious smartphone apps for families from the Stealjob/Knspy Donot team. When installed, the rogue app prompts for elevated Android access permissions, then records screen and keyboard input. Attackers tag team with email, and even try to get better at language localization to seem more legitimate (their French wasn’t very good in earlier attempts).
Another thing, PowerShell is the rather new darling for doing bad things on computer targets. Due to more extensive capabilities, it now can provide a host of functionality that can wreak havoc and provides a useful control panel for threat actors like file exfiltration, download of future payloads and interaction with C&C servers.
And if PowerShell is the new hotness on end-user computers, it’s just that much better on a Windows server. That’s almost game over for an affected server, and attackers have definitely noticed this year, crafting ever-more-powerful assaults against the platform.
Not to be outdone, we still have the perennial low-level target: UEFI. ESET researchers recently found a new entrant called ESPecter that alters the boot process via its ESP component, ramping up super-stealthy malware hiding spots that give security software fits.
How do you defend against these kinds of malware? Surprisingly, simple mistakes like spelling errors are still baked into the malicious exploits, like one that misspelled “backdoor” and then copied the misspelling to multiple files, thereby providing a strong thread of a clue.
Ironically, in most of the investigations highlighted, it’s striking how many pieces in the puzzle came together ultimately due to a “fortuitous discovery”: that means the researchers got lucky somewhere along the way. This may also mean finding something obvious posted on the public web that helps identify the malware authors by usernames still left on social media somewhere that clearly links to the operator identities. It’s funny, in the shadowy workings of the researcher’s palette, how often luck reigns.
Speaking of threat actors for hire, special mention goes to the name contest that must’ve been behind the “Operation Hangover” hacker-for-hire group, regardless of their level of success, which I suppose may be related in some way to the clues represented therein.
We’re looking forward to Virus Bulletin next year in Prague – we hope.
Anatomy of native IIS malware (available also as a series of articles and a white paper on WeLiveSecurity)
Sandworm: reading the indictment between the lines (see also this research on WeLiveSecurity)
Security: the hidden cost of Android stalkerware (available also as an article and a white paper here on WeLiveSecurity)
“Fool Us!”, or is it “Us Fools!”? … 11 “Fools” years later…

Business
Prosecutors seek from 40 to 50 years in prison for Sam Bankman-Fried for cryptocurrency fraud
Published
4 months agoon
March 15, 2024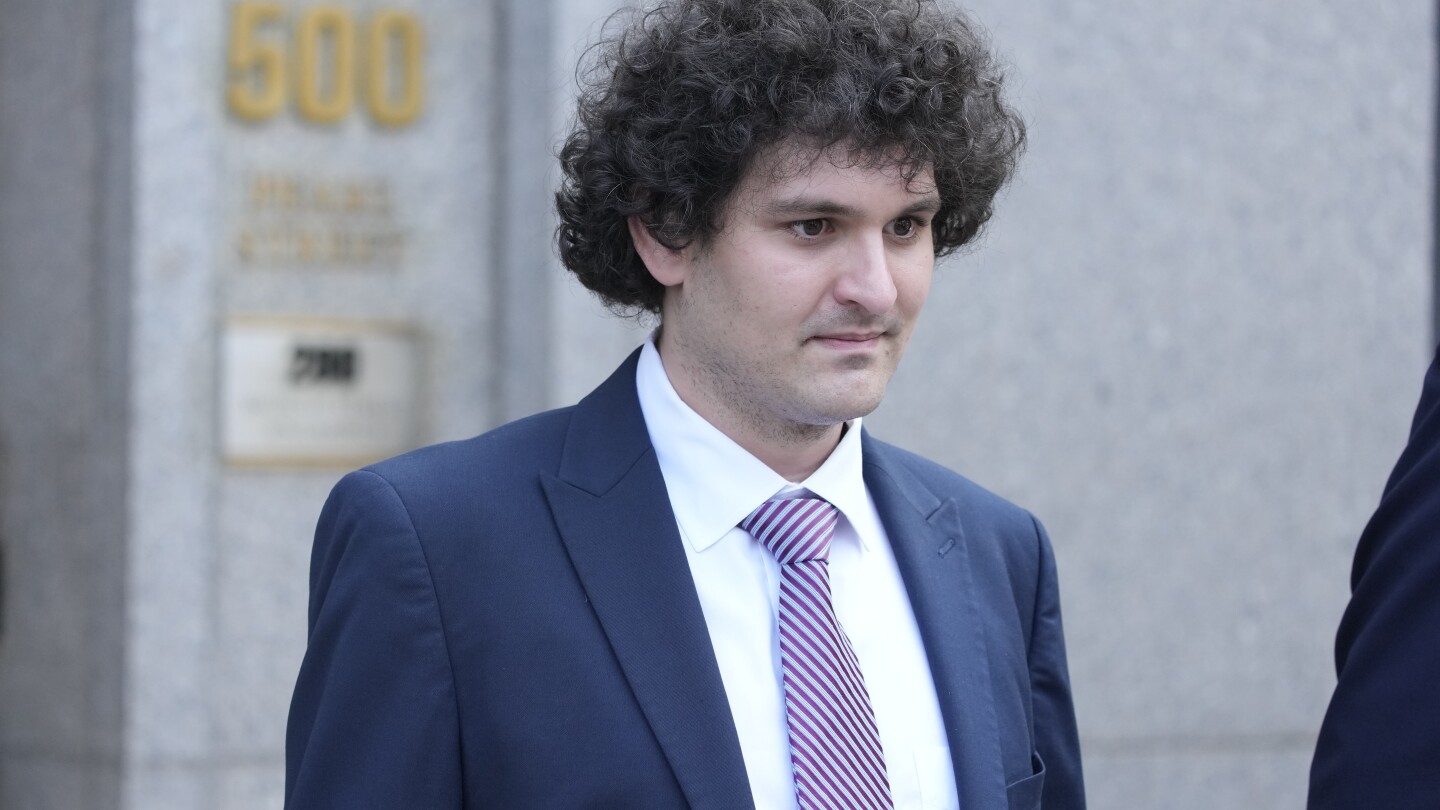
By LARRY NEUMEISTER
NEW YORK (AP) — FTX founder Sam Bankman-Fried’s orchestration of one of history’s largest financial frauds in his quest to dominate the cryptocurrency world deserves a prison sentence of 40 to 50 years, federal prosecutors on Friday told a federal judge.
Prosecutors made the recommendation in papers filed in Manhattan federal court in advance of a March 28 sentencing, where a judge will also consider a 100-year prison sentence recommended by the court’s probation officers and a request by defense lawyers for leniency and a term of imprisonment not to exceed single digits.
Bankman-Fried, 32, was convicted in November on fraud and conspiracy charges after his dramatic fall from a year earlier when he and his companies seemed to be riding a crest of success that had resulted in a Super Bowl advertisement and celebrity endorsements from stars like quarterback Tom Brady and comedian Larry David.
Some of his biggest successes, though, resulted from stealing at least $10 billion from investors and customers between 2017 and 2022 to buy luxury real estate, make risky investments, dispense outsized charitable donations and political contributions and to buy praise from celebrities, prosecutors said.
“His life in recent years has been one of unmatched greed and hubris; of ambition and rationalization; and courting risk and gambling repeatedly with other people’s money. And even now Bankman-Fried refuses to admit what he did was wrong,” prosecutors wrote.
“Having set himself on the goal of amassing endless wealth and unlimited power — to the point that he thought he might become President and the world’s first trillionaire — there was little Bankman-Fried did not do to achieve it,” prosecutors said.
They said crimes reflecting a “brazen disrespect for the rule of law” had depleted the retirement funds and nest eggs of people who could least afford to lose money, including some in war-torn or financially insecure countries, and had harmed others who sought to “break generational poverty” only to be left “devastated” and “heartbroken.”
“He knew what society deemed illegal and unethical, but disregarded that based on a pernicious megalomania guided by the defendant’s own values and sense of superiority,” prosecutors said.
Bankman-Fried was extradited to the United States in December 2022 from the Bahamas after his companies collapsed a month earlier. Originally permitted to remain at home with his parents in Palo Alto, California, he was jailed last year weeks before his trial after Judge Lewis A. Kaplan concluded that he had tried to tamper with trial witnesses.
In their presentence submission, prosecutors described Bankman-Fried’s crimes as “one of the largest financial frauds in history, and what is likely the largest fraud in the last decade.”
“The defendant victimized tens of thousands of people and companies, across several continents, over a period of multiple years. He stole money from customers who entrusted it to him; he lied to investors; he sent fabricated documents to lenders; he pumped millions of dollars in illegal donations into our political system; and he bribed foreign officials. Each of these crimes is worthy of a lengthy sentence,” they wrote.
They said his “unlawful political donations to over 300 politicians and political action groups, amounting to in excess of $100 million, is believed to be the largest-ever campaign finance offense.”
And they said his $150 million in bribes to Chinese government officials was one of the single largest by an individual.
“Even following FTX’s bankruptcy and his subsequent arrest, Bankman-Fried shirked responsibility, deflected blame to market events and other individuals, attempted to tamper with witnesses, and lied repeatedly under oath,” prosecutors said, citing his trial testimony.
Two weeks ago, Bankman-Fried attorney Marc Mukasey attacked a probation office recommendation that their client serve 100 years in prison, saying a sentence of that length would be “grotesque” and “barbaric.”
He urged the judge to sentence Bankman-Fried to just a few years behind bars after calculating federal sentencing guidelines to recommend a term of five to 6 1/2 years in prison.
“Sam is not the ‘evil genius’ depicted in the media or the greedy villain described at trial,” Mukasey said, calling his client a “first-time, non-violent offender, who was joined in the conduct at issue by at least four other culpable individuals, in a matter where victims are poised to recover — were always poised to recover — a hundred cents on the dollar.”
Mukasey said he will respond to the prosecutors’ claims in a filing next week.
Cyber Security
Biden to create cybersecurity standards for nation’s ports as concerns grow over vulnerabilities
Published
5 months agoon
February 21, 2024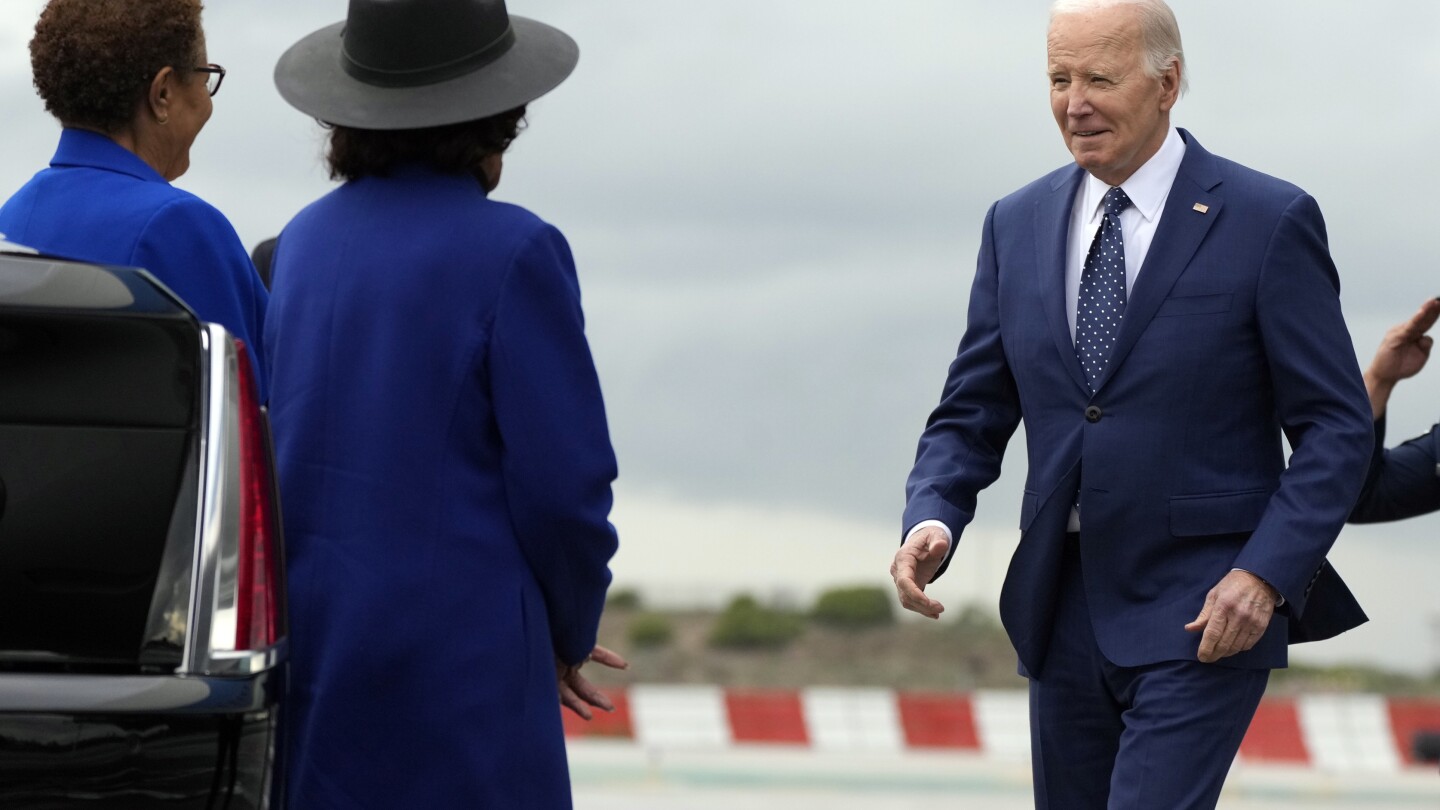
WASHINGTON (AP) — President Joe Biden on Wednesday signed an executive order and created a federal rule aimed at better securing the nation’s ports from potential cyberattacks.
The administration is outlining a set of cybersecurity regulations that port operators must comply with across the country, not unlike standardized safety regulations that seek to prevent injury or damage to people and infrastructure.
“We want to ensure there are similar requirements for cyber, when a cyberattack can cause just as much if not more damage than a storm or another physical threat,” said Anne Neuberger, deputy national security adviser at the White House.
Nationwide, ports employ roughly 31 million people and contribute $5.4 trillion to the economy, and could be left vulnerable to a ransomware or other brand of cyberattack, Neuberger said. The standardized set of requirements is designed to help protect against that.
The new requirements are part of the federal government’s focus on modernizing how critical infrastructure like power grids, ports and pipelines are protected as they are increasingly managed and controlled online, often remotely. There is no set of nationwide standards that govern how operators should protect against potential attacks online.
The threat continues to grow. Hostile activity in cyberspace — from spying to the planting of malware to infect and disrupt a country’s infrastructure — has become a hallmark of modern geopolitical rivalry.
For example, in 2021, the operator of the nation’s largest fuel pipeline had to temporarily halt operations after it fell victim to a ransomware attack in which hackers hold a victim’s data or device hostage in exchange for money. The company, Colonial Pipeline, paid $4.4 million to a Russia-based hacker group, though Justice Department officials later recovered much of the money.
Ports, too, are vulnerable. In Australia last year, a cyber incident forced one of the country’s largest port operators to suspend operations for three days.
In the U.S., roughly 80% of the giant cranes used to lift and haul cargo off ships onto U.S. docks come from China, and are controlled remotely, said Admiral John Vann, commander of the U.S. Coast Guard’s cyber command. That leaves them vulnerable to attack, he said.
Late last month, U.S. officials said they had disrupted a state-backed Chinese effort to plant malware that could be used to damage civilian infrastructure. Vann said this type of potential attack was a concern as officials pushed for new standards, but they are also worried about the possibility for criminal activity.
The new standards, which will be subject to a public comment period, will be required for any port operator and there will be enforcement actions for failing to comply with the standards, though the officials did not outline them. They require port operators to notify authorities when they have been victimized by a cyberattack. The actions also give the Coast Guard, which regulates the nation’s ports, the ability to respond to cyberattacks.
Business
Why Was Sam Altman Fired? Possible Ties to China D2 (Double Dragon) Data from Hackers
Published
8 months agoon
November 19, 2023
Theories are going around the internet why Sam Altman was fired. On an insider tech forum (Blind) – one person claims to know by third-hand account and how this news will trickle into the media over the next couple of weeks.
It’s said OpenAI had been using data from D2 to train its AI models, which includes GPT-4. This data was obtained through a hidden business contract with a D2 shell company called Whitefly, which was based in Singapore. This D2 group has the largest and biggest crawling/indexing/scanning capacity in the world 10x more than Alphabet Inc (Google), hence the deal so Open AI could get their hands on vast quantities of data for training after exhausting their other options.
The Chinese government became aware of this arrangement and raised concerns with the Biden administration. As a result, the NSA launched an investigation, which confirmed that OpenAI had been using data from D2. Satya Nadella, the CEO of Microsoft, which is a major investor in OpenAI, was informed of the findings and ordered Altman’s removal.
There was also suggestion that Altman refused to disclose this information to the OpenAI board. This lack of candor ultimately led to his dismissal and is what the board publicly alluded to when they said “not consistently candid in his communications with the board.”
To summarize what happened with Sam Altman’s firing:
1. Sam Altman was removed from OpenAI due to his ties to a Chinese cyber army group.
2.OpenAI had been using data from D2 to train its AI models.
3. The Chinese government raised concerns about this arrangement with the Biden administration.
4. The NSA launched an investigation, which confirmed OpenAI’s use of D2 data.
5. Satya Nadella ordered Altman’s removal after being informed of the findings.
6. Altman refused to disclose this information to the OpenAI board.
We’ll see in the next couple of weeks if this story holds up or not.